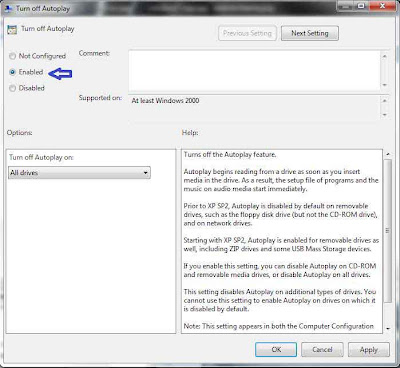
The Windows 7 Disk Management tool provides a simple interface for managing partitions and volumes.
Here’s an easy way to create a new partition on your disk.
Here’s an easy way to create a new partition on your disk.
- Open the Disk Management console by typing diskmgmt.msc at an elevated command prompt.
- In Disk Management’s Graphical view, right-click an unallocated or free area, and then clickNew Simple Volume. This starts the New Simple Volume Wizard. (Note: If you need to createunallocated space,Read the Welcome page and then click Next.
- The Specify Volume Size page specifies the minimum and maximum size for the volume in
megabytes and lets you size the volume within these limits. Size the partition in megabytes
using the Simple Volume Size field and then click Next.On the Assign Drive Letter Or Path page, specify whether you want to assign a drive letter
or path and then click Next. The available options are as follows: - Assign The Following Drive Letter Select an available drive letter in the selection listprovided. By default, Windows 7 selects the lowest available drive letter and excludesreserved drive letters as well as those assigned to local disks or network drives.Mount In The Following Empty NTFS Folder Choose this option to mount the partitionin an empty NTFS folder. You must then type the path to an existing folder or click Browsetosearch for or create a folder to use.Do Not Assign A Drive Letter Or Drive Path Choose this option if you want to createthe partition without assigning a drive letter or path. Later, if you want the partition to beavailable for storage, you can assign a drive letter or path at that time.
- Use the Format Partition page to determine whether and how the volume should be formatted. If you want to format the volume, choose Format This Volume With The Following Settings,and then configure the following options:File System Sets the file system type as FAT, FAT32, or NTFS. NTFS is selected by defaultin most cases. If you create a file system as FAT or FAT32, you can later convert itto NTFS by using the Convert utility. You can’t, however, convert NTFS partitions to FAT or FAT32.Allocation Unit Size Sets the cluster size for the file system. This is the basic unit in whichdisk space is allocated. The default allocation unit size is based on the size of thevolume and, by default, is set dynamically prior to formatting. To override this feature,you can set the allocation unit size to a specific value. If you use many small files, youmight want to use a smaller cluster size, such as 512 or 1,024 bytes. With these settings, small files use less disk space.Volume Label Sets a text label for the partition. This label is the partition’s volume nameand by default is set to New Volume. You can change the volume label at any time byright-clicking the volume in Windows Explorer, choosing Properties, and typing a new valuein the Label field provided on the General tab.Perform A Quick Format Tells Windows 7 to format without checking the partition forerrors. With large partitions, this option can save you a few minutes. However, it’s usuallybetter to check for errors, which enables Disk Management to mark bad sectors on the diskand lock them out.Enable File And Folder Compression Turns on compression for the disk. Built-incompression is available only for NTFS. Under NTFS, compression is transparent to users andcompressed files can be accessed just like regular files. If you select this option, files anddirectories on this drive are compressed automatically.
- Click Next, confirm your options, and then click Finish. The Windows 7 Disk
Management tool will now show the space configured as a new partition.